One’s own rigid interpretation of a situation prevents one from recognizing what is needed to make it go ahead. There are quick conflicts and rifts between people who should work together to solve a problem.
How do we deal with fixed interpretations in coaching or team development?
RESOLVING FIXED INTERPRETATION – DEALING WITH IT IN COACHING
THINKING AND THINKING FEELINGS – THE LOOP OF INTERPRETATION / “GLASSES”
The perception ladder or interpretation loop is an explanatory model for how communication often takes place and which internal dynamics and feedback loops can occur. If system law violations occur, this interpretation loop is more intensive. 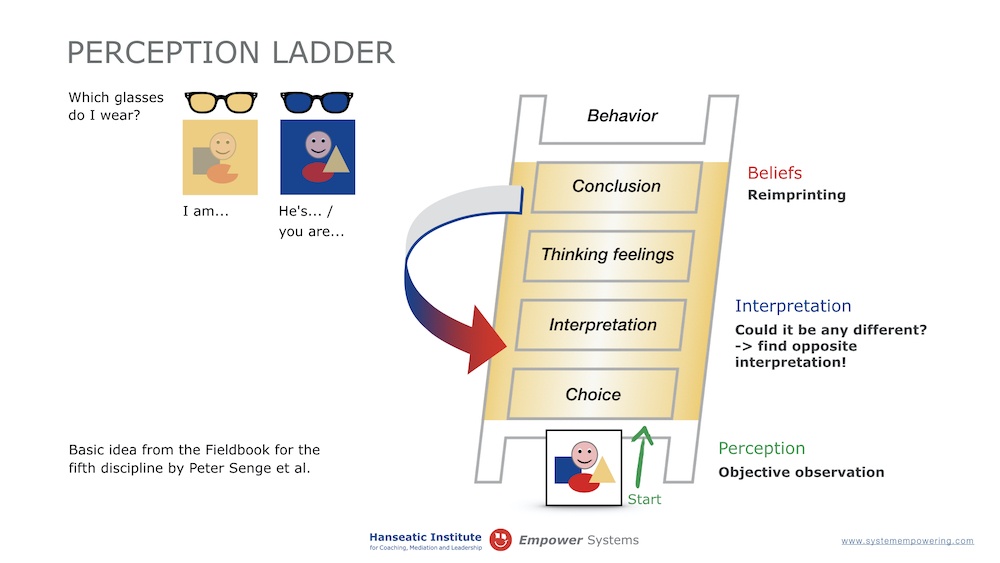
The reflexive loop (feedback):
My beliefs and conclusions influence which data I choose next time and how I interpret it.
An example: In a meeting or lecture someone yawns
1. Selection of the data: A participant yawns.
2. Interpretation: disinterest or boredom (possible other typical interpretations would be): Lack of oxygen or the participant is tired)
3. Feelings of thinking: anger, fear, insecurity …
4. conclusions and beliefs: Either: I am not good enough, I bore him – when I refer to myself. Or: The other is d…, he is always like that etc. – when I refer to him.
5. action based on the developed convictions: Either I turn red, try harder or I become aggressive or I turn away from the other person.
6. is again 1. – New data are selected (feedback loop, because the beliefs also influence the data selection). If the other person then looks out of the window or writes in his notebook, the “glasses” are confirmed: I am like this or he is like this.
It can no longer be imagined that the other might have made notes out of interest or looked out of the window to process what he had heard.
A life without additional interpretations or conclusions is not possible, because interpretations serve e.g. to determine in fractions of seconds whether a danger threatens or not.
However, it is important to know that one interprets that this does not have to be reality, but that it can also be different.
It is also useful to think about getting out of this loop. There are three possibilities.
Interpretation is not perception, because it is filtered.
What have you objectively observed? How would a video camera record it?
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PERCEPTION AND INTERPRETATION
If you look at the adjacent person, what do you perceive?
In general, I get the following answers: She is thoughtful, withdrawn, introverted or purposeful.
These answers are not perceptions, but interpretations. Everyone has his or her own interpretations, and if they do not fit in with the other person, it can be argued about. But not about a perception.
So what is a perception?
She sits, her upper body is bent forward by about 15 degrees, her hands touch each other, her left hand is bent to the right and touches her chin…
Excercise: Create a table and in the left column write typical interpretations of yourself as you describe others. Put your perception in the middle column. In the right column write down possible further interpretations.
| Interpretation | Perception (concrete) | Further interpretation |
| unsteady | trembling in the voice | flustered |
| on the run | Posture bent forward | interested |
| thoughtfully | Chin resting on the hand | sad |
| rejection | Hands crossed in front of abdomen | snug |
| ? | ? | ? |
| ? | ? | ? |
From this task it may become clear to you how dangerous it is to draw a certain conclusion from a posture. Ask yourself or your client: “What could another interpretation or conclusion look like?
Often there is only one interpretation. So ask yourself/your client the question:
Could it also be different?
What could be another interpretation?
Find a contrary interpretation. If, for example, a listener yawns, this does not necessarily mean that the listener is bored. It could also be that he slept badly or that there is a lack of oxygen in the room.
Edit your beliefs, beliefs and conclusions by first uncovering them and then changing them.
There are beliefs that can be easily changed and others that can only be changed through coaching.
The thinking feelings can be influenced by a changed thinking, for example a different interpretation of the situation, but the resulting basic feelings are not dissolved.
The basic feelings are the deeper feelings that exist when one does not think.
There are several reasons for it, if the interpretations and/or conclusions are negative and stand as cemented. Let us take a look at the interpretation loop, which describes in a model way how interpretations and conclusions come about. At the bottom of the picture, at the foot of the ladder, everything is still objective. When information is selected, it becomes subjective.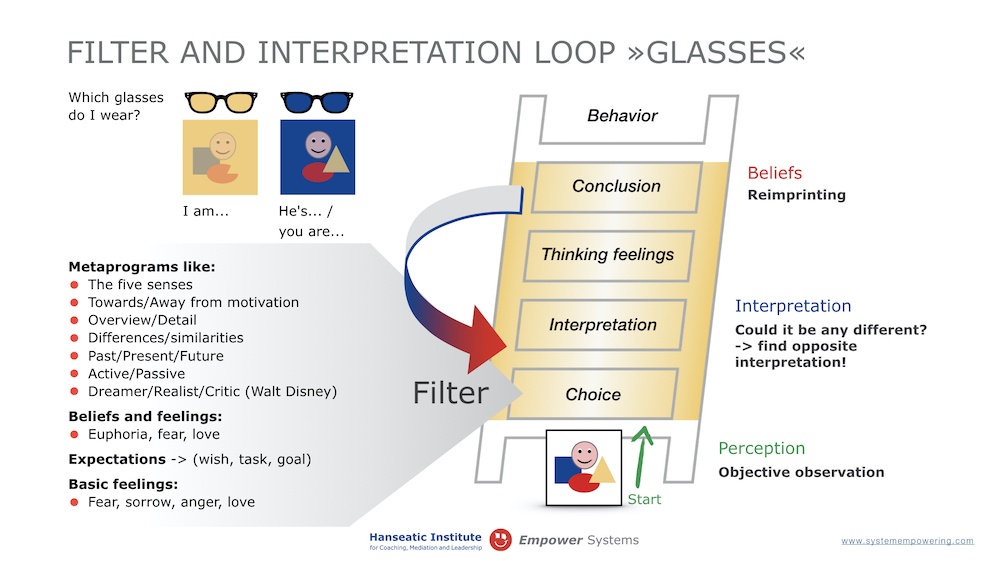
– Subjective selection / filter: Each person has different internal programs, how the information is recorded and what is filtered out. This includes the metaprograms. Each person records information in a very individual way. This specific way of perception and processing has been developed by the environmental conditions and the role model function of relevant reference persons in each individual.
These metaprograms or filters function as perception grids and preferred processing mechanisms and serve primarily to simplify perception and analysis processes. This has advantages but also disadvantages. On the one hand, filters are used to filter out information. On the other hand, they can also act as catalysts and generate amplification.
All metaprograms are potentially available to everyone, and with a little practice they can be made more flexible and used more often.
The most common metaprograms are the following:
The five senses: seeing, hearing, feeling, smelling, tasting
Do I need pictures or a spoken word for information processing? What is my preferred sensory system? Which sensory channel is rather underrepresented?
Motivational direction: Towards – away from
describes the starting point of motivation, i.e. whether the behaviour is rather determined by a “towards” (a goal) or by a “away” from (the old situation).
Information size: Overview – Detail
This metaprogram describes the order in which people prefer to absorb knowledge. First the essential details and examples and then the larger whole or rather the other way round, i.e. first an overview and then the details.
Evaluation: Differences – Similarities
If I take rather the differences was or is the focus rather on similarities. If two things are compared, what is the first thing to notice?
Time orientation: past, present, future
Is the focus of perception more in the past, present or future?
Drive: active – passive
Does someone actively approach something, act spontaneously and react immediately, or does he rather wait, observe, consider and then act only after a while or not at all?
Dreamer, Realist, Critic (Walt Disney)
The dreamer is the visionary, everything is possible. The realist is the implementer, sees the milestones and goals. The critic is the consultant who sees concerns and negative effects.
There are more filters. These include beliefs and feelings of thought such as euphoria, fear or love. The proverbs: The pink glasses or love or fear or anger makes blind, express these filters. Conclusions that arise from the interpretation loop through interpretation are also strong filters. These conclusions “glasses” – the stalled interpretation lead to the perception that certain information is no longer perceived and other information is colored.
Convictions and mental feelings:
– Euphoria, fear, love, formative experiences
Impressions, beliefs and moral concepts can be dissolved or changed in coaching by the methods of new imprinting/reimprinting or empowering.
Expectations -> (wish, task, goal)
Having expectations means waiting, because normally the other person does not know what expectation is addressed to them. That is why it is important to formulate expectations as wishes, tasks or goals.
Basic feelings that have arisen, for example, as a result of system law violations:
– Fear, grief, anger, love
Unresolved system law violations lead to basic feelings such as suffering, fear, grief and anger and create “glasses” with feelings of thought. These feelings are also strong filters like the mental feelings.
What happens to humans in the event of a system violation?
If someone is excluded, disrespected, unjust or pushed forward, there is a four-step process that happens to the injured person.
1. Basic feelings I: First an injured basic feeling I develops. Typical descriptions of injured basic feelings are stomach pains, muscles tense, soft knees, trembling, pressure in the stomach, hot, cold, tears shooting into the eyes, trembling, heart palpitations, etc. …
Depending on the severity of the injury, these feelings may be stronger or weaker. Almost everyone knows a not so strong feeling when someone pushes himself forward in traffic.
2. Basic feeling II: Shortly afterwards (often only one second later) the basic feeling II arises, namely anger or rage.
3. Thinking: Only after the basic feelings have developed does the person begin to think about the injury. It is interpreted and concluded depending on which “glasses” the person already wears.
4. Thinking feelings: This thinking and interpreting creates a feeling which I call thinking feelings. It is in direct interaction with thinking. These feelings of thinking are often described as follows: I feel ignored, not respected, it is unjust …
If this first violation of system law is not resolved, it will usually lead to a re-injury and escalate further. In the same way, the “spectacles” are always further embossed. If system law violations are present, the “glasses” – the fixed interpretation – cannot simply be resolved, but must be processed in parallel with the resolution of the system law violations.
SUMMARY: PROCEDURE IN COACHING / MEDIATION / SYSTEM EMPOWERING
– Communicating knowledge about the interpretation loop
– Communicate knowledge about the system laws and the impact of an SG violation.
– To provide knowledge on how to resolve system law violations.
– Present filters.
– Find out whether it is about beliefs or imprints with corresponding feelings of thought -> Empowering
– Find out if it’s about filters -> Make filters or metaprograms more flexible
– Find out whether it is about expectations -> uncovering expectations and transforming them into goals, wishes, demands
– Find out whether it is a question of system law violations with basic feelings and “glasses” with mental feelings shaped by them -> dissolve system law violations, update “glasses” in parallel.

